cgradient
Gradient of a multivariate, scalar-valued function using the central difference approximation.
Back to Numerical Differentiation Toolbox Contents.
Contents
Syntax
g = cgradient(f,x0) g = cgradient(f,x0,h)
Description
g = cgradient(f,x0) numerically evaluates the gradient of 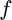 with respect to
with respect to 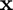 at
at  using the central difference approximation with a default relative step size of
using the central difference approximation with a default relative step size of 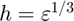 , where
, where 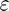 is the machine zero.
is the machine zero.
g = cgradient(f,x0,h) numerically evaluates the gradient of 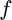 with respect to
with respect to 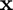 at
at  using the central difference approximation with a user-specified relative step size
using the central difference approximation with a user-specified relative step size 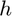 .
.
Input/Output Parameters
| Variable | Symbol | Description | Format | |
| Input | f | multivariate, scalar-valued function ( |
1×1 function_handle |
|
| x0 | evaluation point | n×1 double |
||
| h | (OPTIONAL) relative step size (defaults to $h=\varepsilon^{1/3}$) | 1×1 double |
||
| Output | g | gradient of |
n×1 double |
Note
- This function requires
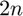 evaluations of
evaluations of 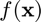 .
.
Example
Approximate the gradient of 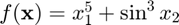 at
at 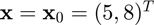 using the cgradient function, and compare the result to the true result of
using the cgradient function, and compare the result to the true result of
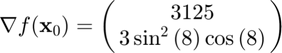
Approximating the gradient,
f = @(x) x(1)^5+sin(x(2))^3; x0 = [5;8]; g = cgradient(f,x0)
g =
1.0e+03 *
3.1250
-0.0004
Calculating the error,
error = g-[3125;3*sin(8)^2*cos(8)]
error =
1.0e-06 *
0.3280
0.0020